Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plot lines¶
Plotting lines is handled by pygmt.Figure.plot.
Note
This tutorial assumes the use of a Python notebook, such as IPython or Jupyter Notebook.
To see the figures while using a Python script instead, use
fig.show(method="external") to display the figure in the default PDF viewer.
To save the figure, use fig.savefig("figname.pdf") where "figname.pdf"
is the desired name and file extension for the saved figure.
import pygmt
Plot lines¶
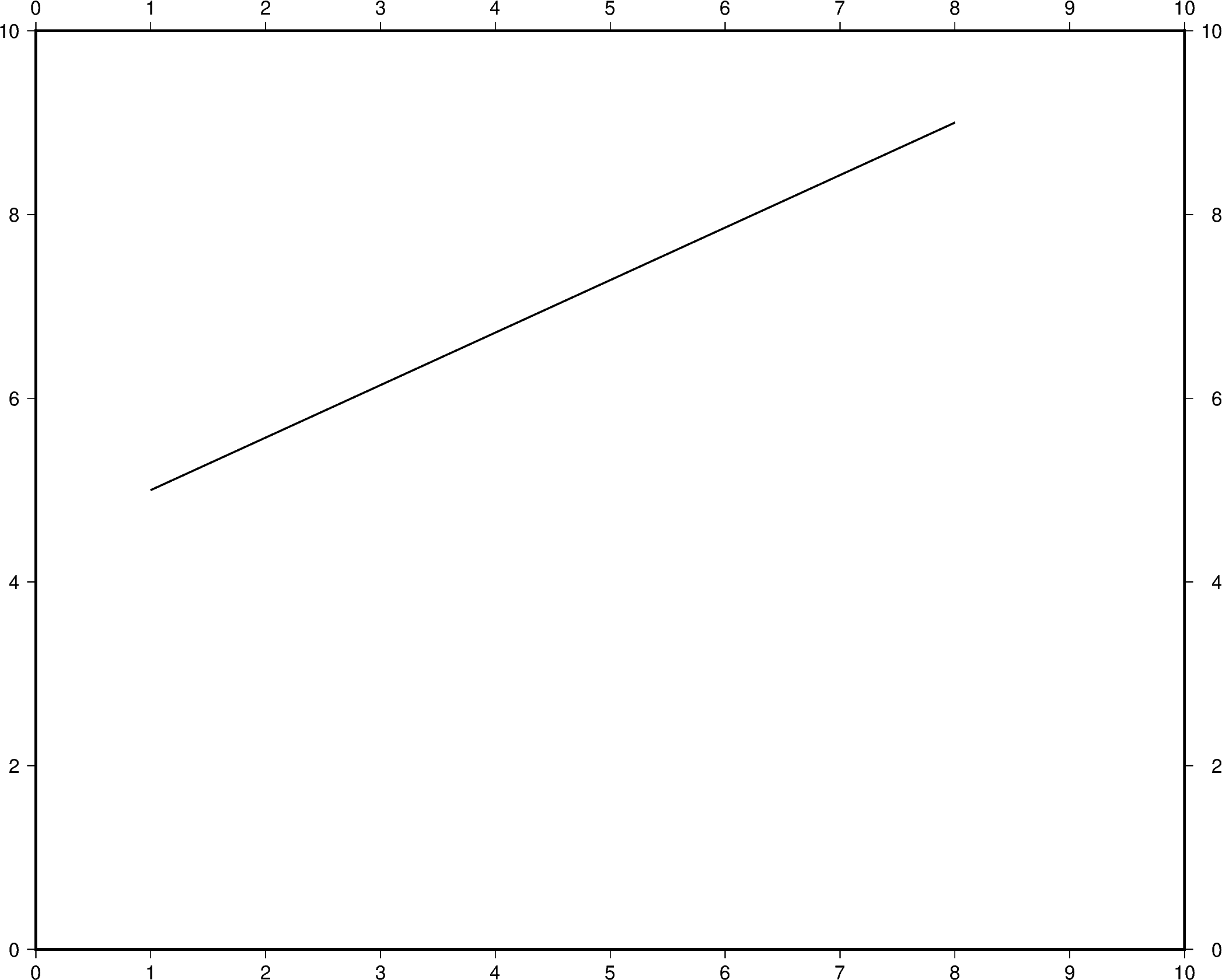
Create a Cartesian figure using projection parameter and set the axis scales
using region (in this case, each axis is 0-10). Pass a list of x and y
values to be plotted as a line.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 8],
y=[5, 9],
pen="1p,black",
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
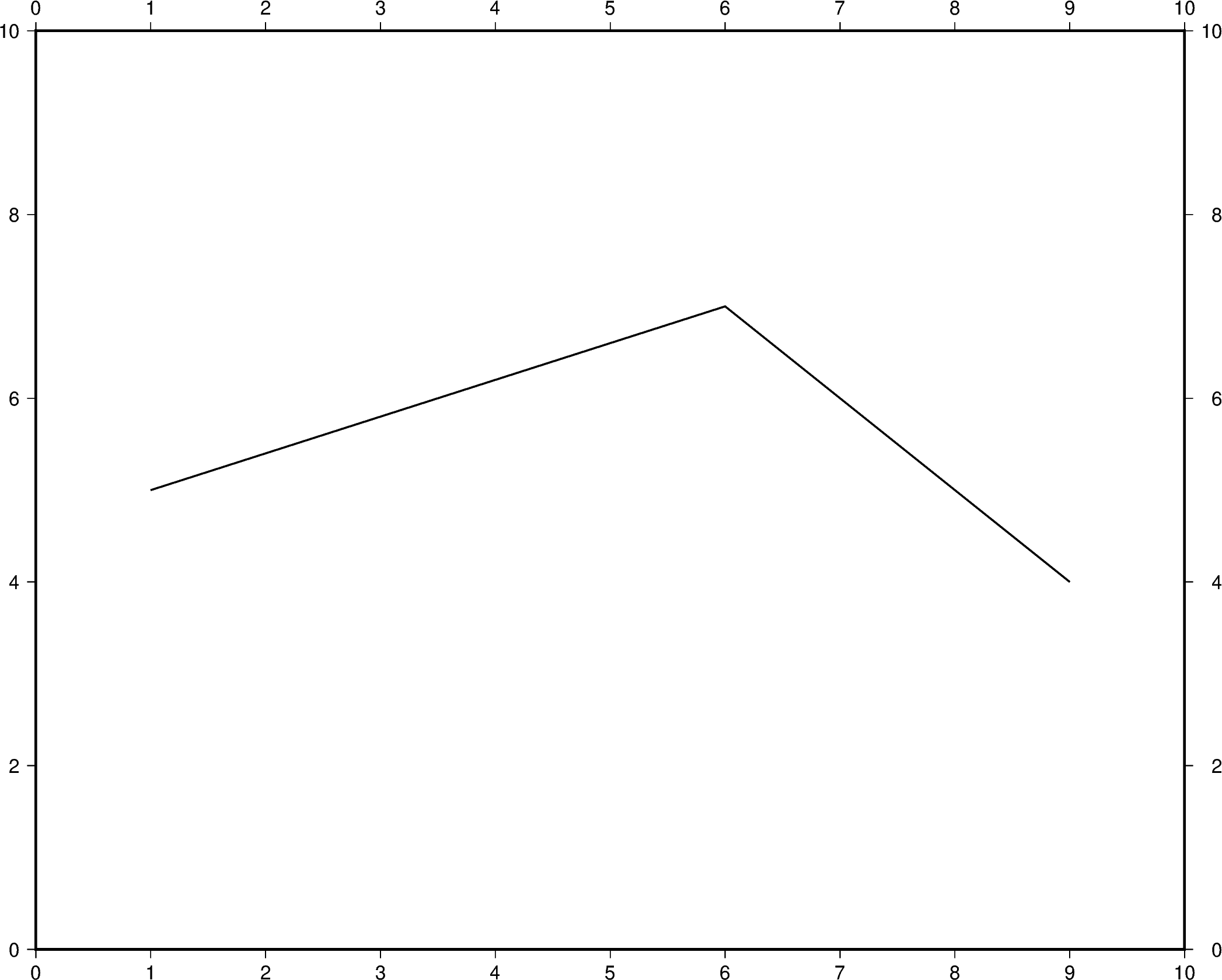
Additional line segments can be added by including additional values for x
and y.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 6, 9],
y=[5, 7, 4],
pen="1p,black",
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
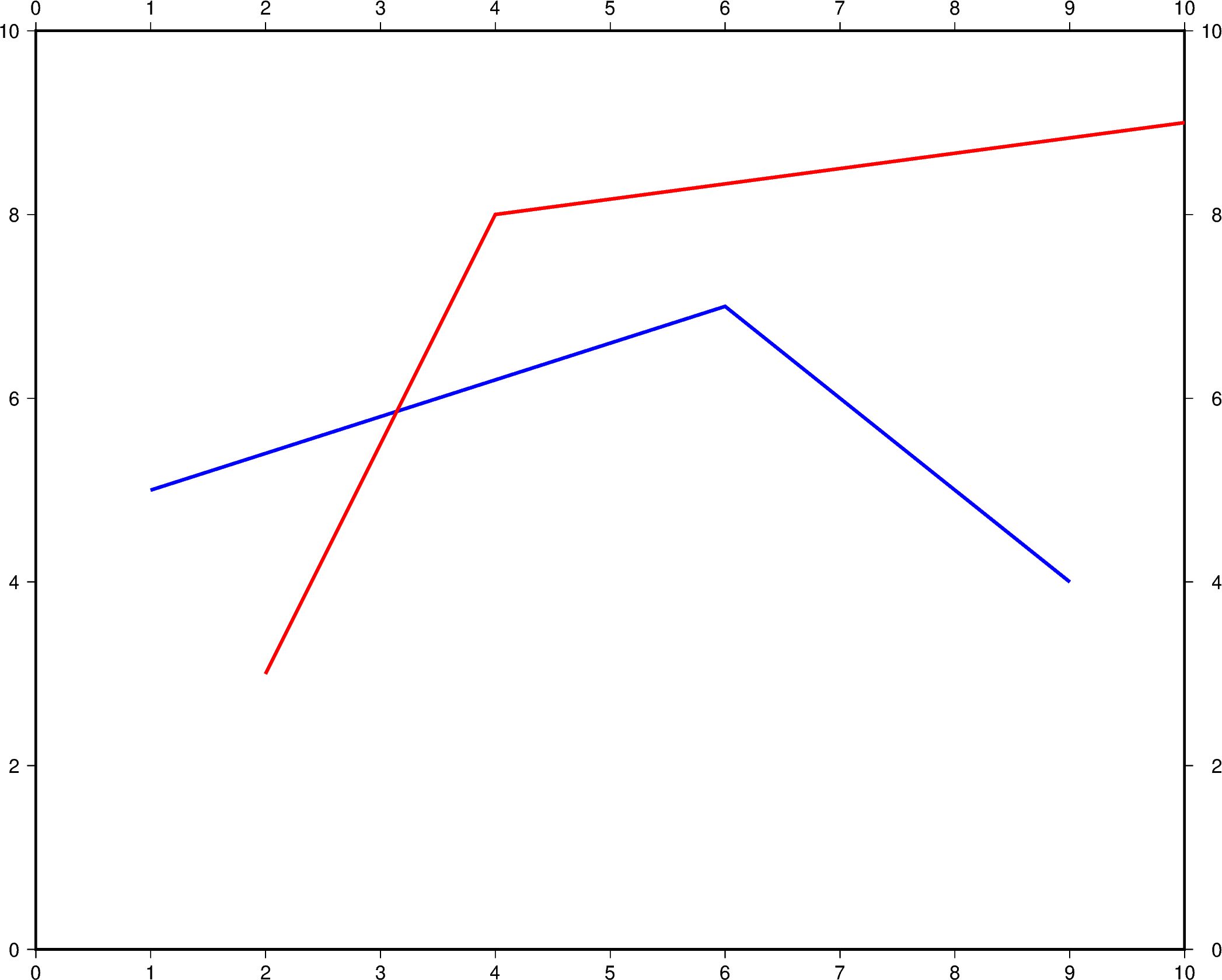
To plot multiple lines, pygmt.Figure.plot needs to be used for each
additional line. Arguments such as region, projection, and frame do
not need to be repeated in subsequent uses.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 6, 9],
y=[5, 7, 4],
pen="2p,blue",
)
fig.plot(x=[2, 4, 10], y=[3, 8, 9], pen="2p,red")
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Change line attributes¶
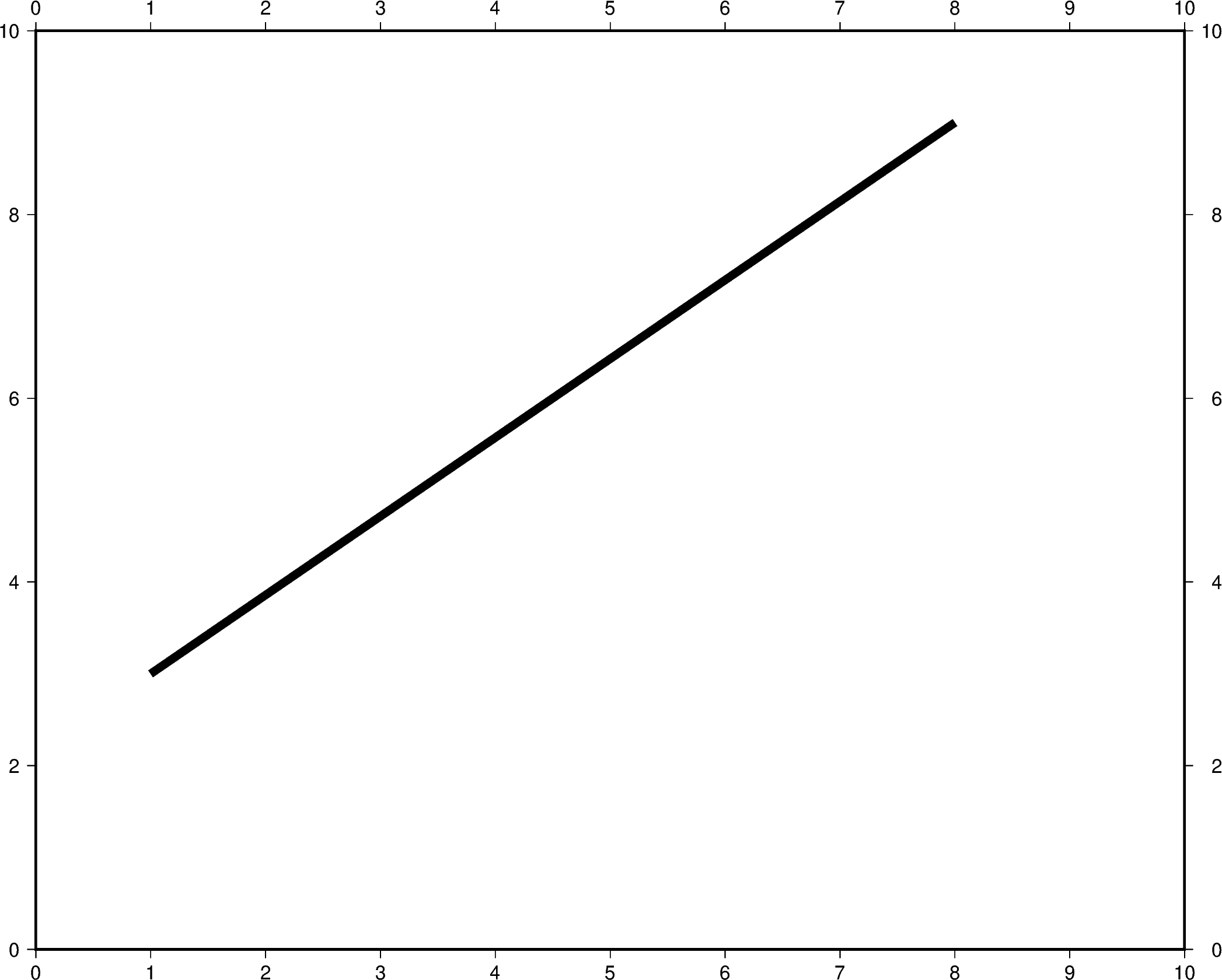
The line attributes can be set by the pen parameter. pen takes a string
argument with the optional values width,color,style.
In the example below, the pen width is set to 5p, and with black as the
default color and solid as the default style.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 8],
y=[3, 9],
pen="5p",
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
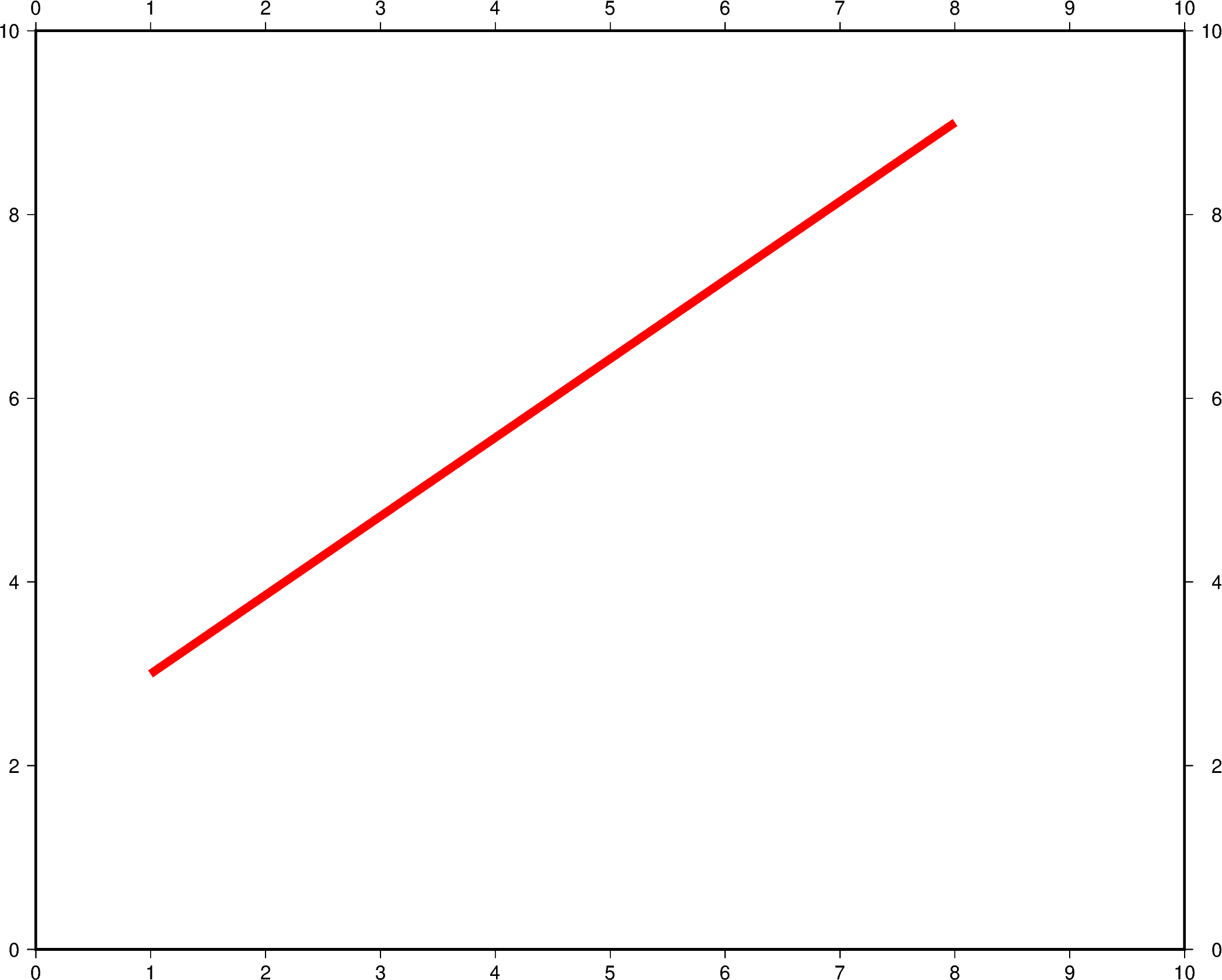
The line color can be set and is added after the line width to the pen parameter.
In the example below, the line color is set to red.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 8],
y=[3, 9],
pen="5p,red",
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
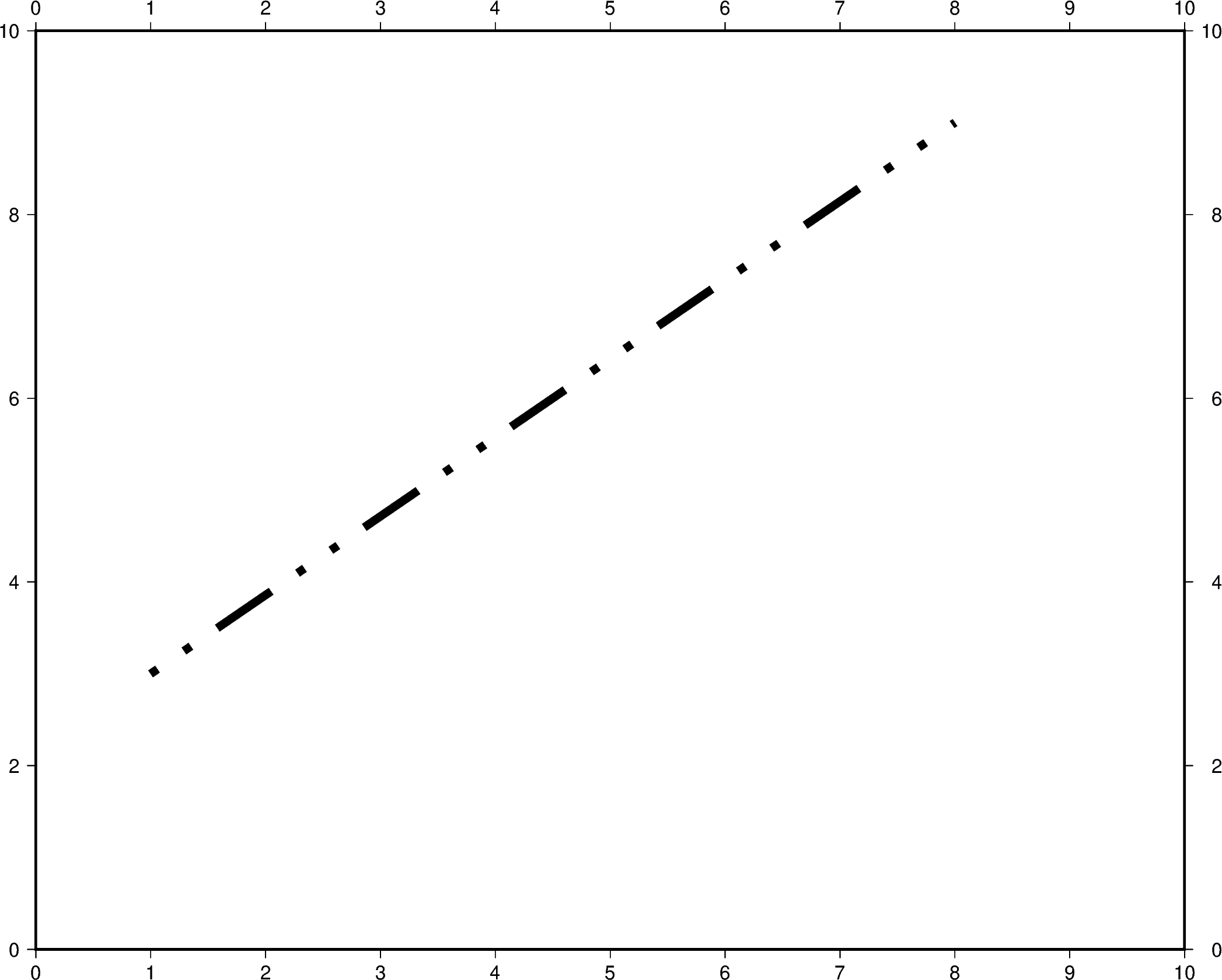
The line style can be set and is added after the line width or color to the
pen parameter. In the example below, the line style is set to
..- (dot dot dash), and the default color black is used.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 8],
y=[3, 9],
pen="5p,..-",
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
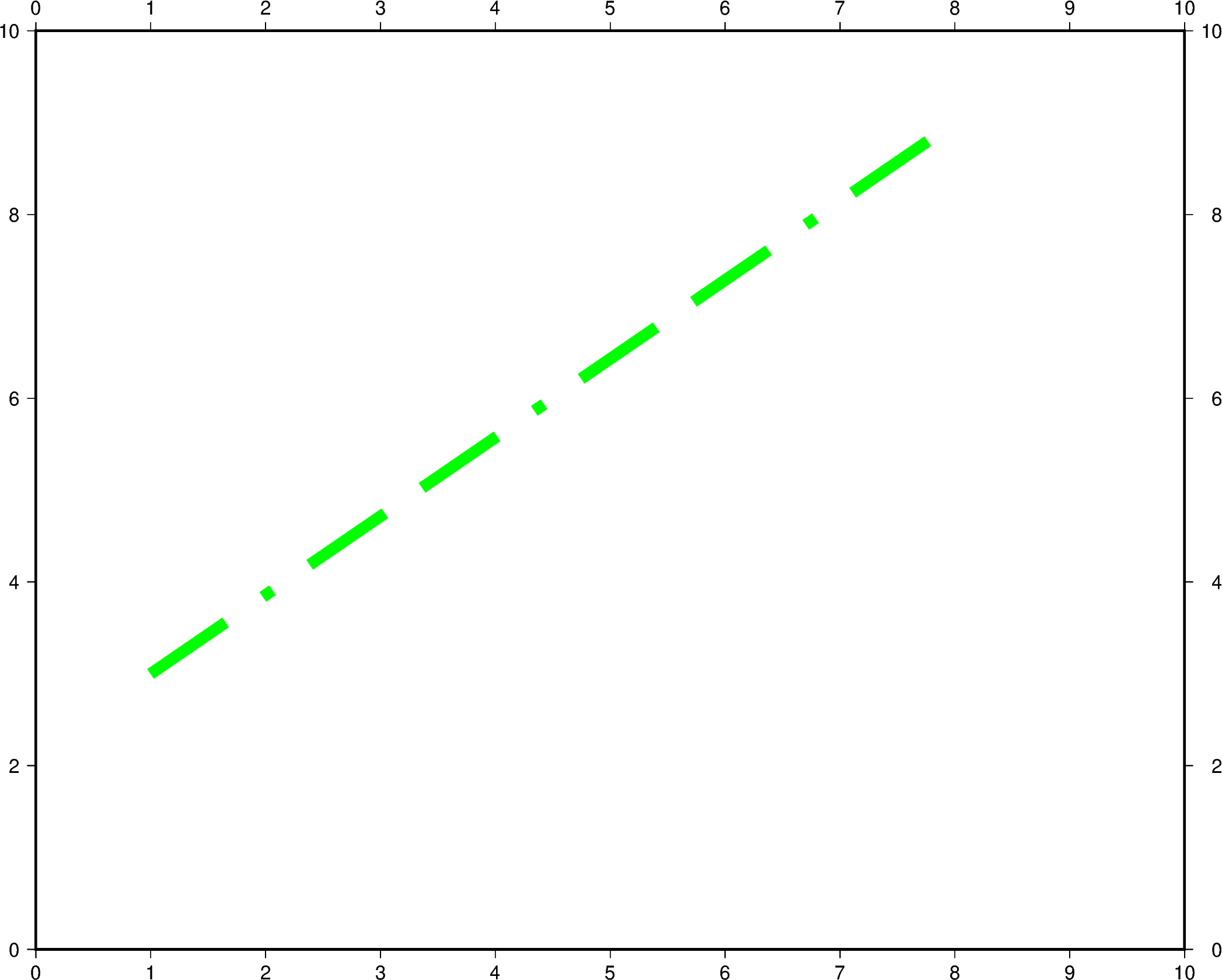
The line width, color, and style can all be set in the same pen parameter. In the
example below, the line width is set to 7p, the color is set to green, and the
line style is -.- (dash dot dash).
For a gallery showing other pen settings, see Line styles.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.plot(
region=[0, 10, 0, 10],
projection="X25c/20c",
frame="a",
x=[1, 8],
y=[3, 9],
pen="7p,green,-.-",
)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 11.396 seconds)